If you’ve ever wondered about the difference between bandwidth and broadband, you’re not alone. It’s a common source of confusion in the world of internet connectivity. So, let’s clear things up right from the start. Bandwidth refers to the amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection in a given amount of time.
On the other hand, broadband is a type of internet connection that provides high-speed access to the internet. Now that we have that out of the way, let’s delve deeper into the fascinating world of bandwidth and broadband and understand how they work together to keep us connected. Let’s get started!
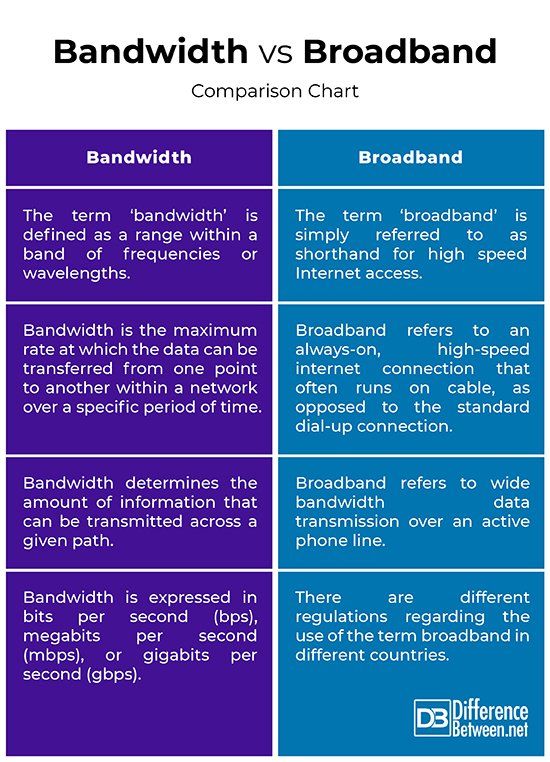
Bandwidth Vs Broadband
| Feature | Bandwidth | Broadband |
| Definition | The maximum rate of data transfer across a network. | A high-capacity transmission medium that can carry multiple signals simultaneously. It encompasses a wide range of frequencies. |
| Speed | Bandwidth is a measure of speed, often expressed in bits per second (bps), kilobits per second (kbps), or megabits per second (Mbps). | Broadband refers to high-speed internet access that is faster than traditional dial-up connections. It provides higher data transfer rates, typically ranging from 256 kbps to several gigabits per second. |
| Transmission Medium | Bandwidth can be used to describe the capacity of any communication channel, including wired (e.g., Ethernet cables) or wireless (e.g., Wi-Fi) connections. | Broadband specifically refers to a high-capacity transmission medium, which can include various technologies such as digital subscriber line (DSL), cable, fiber-optic, and wireless connections. |
| Application | Bandwidth is a general term used to describe the data capacity of a network connection and is not limited to internet access. | Broadband is primarily associated with high-speed internet access, allowing for faster and more efficient data transmission, supporting various online activities such as streaming, online gaming, and video conferencing. |
| Scope | Bandwidth can be narrow or broad, depending on the specific network or communication channel. | Broadband inherently implies a wide range of frequencies and a higher data transfer capacity, offering a broader and more extensive communication capability. |
| Example | A network with a bandwidth of 100 Mbps means it can transfer 100 megabits of data per second. | A broadband internet connection might provide speeds ranging from 25 Mbps to 1 Gbps, offering fast and reliable internet access. |
| Usage | Bandwidth is a measure of capacity and can be used in various contexts, including computing, telecommunications, and networking. | Broadband is specifically associated with high-speed internet access services for residential and commercial users. |
Difference Between Bandwidth and Broadband
When it comes to internet services, you may have come across terms like bandwidth and broadband. These are two concepts that are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. Understanding the difference between bandwidth and broadband can help you make informed decisions about your internet connection and ensure you get the best possible experience. In this article, we will delve into the nuances of bandwidth and broadband, exploring their definitions, how they work, and the key differences between them.
What is Bandwidth?
Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over an internet connection in a given period. It is often measured in bits per second (bps) or multiples of it such as kilobits per second (Kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps). In simpler terms, bandwidth is the capacity or speed at which data can be transferred. The higher the bandwidth, the faster the data can be transmitted.
Bandwidth is like a pipeline through which data flows from the internet to your device. Just like a larger pipeline allows more water to flow through, higher bandwidth enables more data to be transferred. It determines how quickly you can download or upload files, stream videos, play online games, and perform other internet-related tasks.
What is Broadband?
Broadband, on the other hand, refers to a high-speed internet connection that provides wide bandwidth. It is a term used to describe various types of internet connections that offer faster speeds than traditional dial-up connections. Broadband utilizes a wide range of frequencies to transmit data, enabling multiple signals to be carried simultaneously.
Broadband connections use different technologies, such as Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), cable, fiber-optic, and satellite, to deliver high-speed internet access to homes and businesses. These connections are typically “always-on,” meaning they don’t require dialing up or connecting each time you want to use the internet.
The term “broadband” became popular as a way to differentiate the faster internet connections from the older, slower dial-up connections. It offers users the ability to download and upload data at much higher speeds, making it ideal for activities that require significant bandwidth, such as streaming high-definition videos, online gaming, and video conferencing.
Key Differences Between Bandwidth and Broadband
Now that we have a basic understanding of bandwidth and broadband, let’s explore their key differences:
Definition:
- Bandwidth: It refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over an internet connection in a given period.
- Broadband: It is a high-speed internet connection that provides wide bandwidth and utilizes various technologies to deliver fast internet access.
Measurement:
- Bandwidth: It is measured in bits per second (bps) or multiples of it, such as kilobits per second (Kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps).
- Broadband: It is not measured directly but is used to describe internet connections that offer higher speeds than dial-up connections.
Functionality:
- Bandwidth: It determines the speed at which data can be transferred over an internet connection.
- Broadband: It refers to the type of internet connection that provides fast and high-speed access to the internet.
Scope:
- Bandwidth: It is a technical term that focuses on the capacity and speed of data transmission.
- Broadband: It is a broader term that encompasses various types of high-speed internet connections.
While bandwidth and broadband are related, they have distinct meanings and are used in different contexts. Bandwidth is more focused on the speed and capacity of data transmission, while broadband refers to the type of high-speed internet connection that offers wide bandwidth. Understanding these differences can help you make informed decisions about your internet service provider and choose the right plan that meets your needs.
Lastly, it’s important to note that both bandwidth and broadband are crucial factors in determining the performance and speed of your internet connection. Higher bandwidth allows for faster data transfer, while broadband connections provide the infrastructure needed to support such high-speed access. When selecting an internet service provider, it’s essential to consider both factors to ensure you have a reliable and fast internet connection.
Speed vs Bandwidth Explained – Arvig
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between bandwidth and broadband?
Bandwidth and broadband are often used interchangeably, but they refer to different aspects of internet connectivity.
How is bandwidth different from broadband?
Bandwidth refers to the capacity of a network to transmit data, measured in bits per second (bps). It represents the maximum data transfer rate. On the other hand, broadband refers to high-speed internet access that allows for the transmission of large amounts of data simultaneously.
Is bandwidth the same as internet speed?
While bandwidth is a measure of capacity, internet speed refers to how quickly data is transferred from one place to another. Bandwidth determines the maximum speed at which data can be transferred, but other factors like network congestion and latency can affect the actual internet speed experienced by users.
What are the different types of broadband connections?
The main types of broadband connections include Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), cable, fiber-optic, and satellite. These technologies provide high-speed internet access to users through various mediums such as telephone lines, coaxial cables, optical fibers, and wireless satellite connections.
Can bandwidth affect broadband performance?
Yes, bandwidth plays a crucial role in determining broadband performance. Higher bandwidth allows for faster data transmission, resulting in a better internet experience. However, it’s important to note that other factors like network congestion, equipment quality, and service provider limitations can also impact overall broadband performance.
How can I increase my broadband bandwidth?
To increase your broadband bandwidth, you can try the following steps:
1. Contact your internet service provider to inquire about available higher bandwidth plans.
2. Consider upgrading your modem or router to a newer model that supports higher speeds.
3. Optimize your Wi-Fi network by placing the router in a central location, minimizing interference, and using a wired connection whenever possible.
4. Close any unnecessary applications or devices that may be consuming bandwidth in the background.
5. Regularly perform speed tests to monitor your broadband performance and identify any potential issues.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the key difference between bandwidth and broadband lies in their definitions and functionality. Bandwidth refers to the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection, while broadband refers to high-speed internet access that provides a wide range of bandwidth options.
Bandwidth determines the capacity, while broadband encompasses the technology that enables fast internet connectivity. Understanding the distinction between bandwidth and broadband is crucial in order to effectively choose the right internet plan that meets your specific needs.